Webhook
Webhooks allow you to receive document data from your Workflow directly to your server in real-time.
Setting Up Webhooks
Webhooks are ideal when you want to handle events from specific Workflows in your Server. This allows for more granular control and easier integration with specific business processes.
To set up a Webhook:
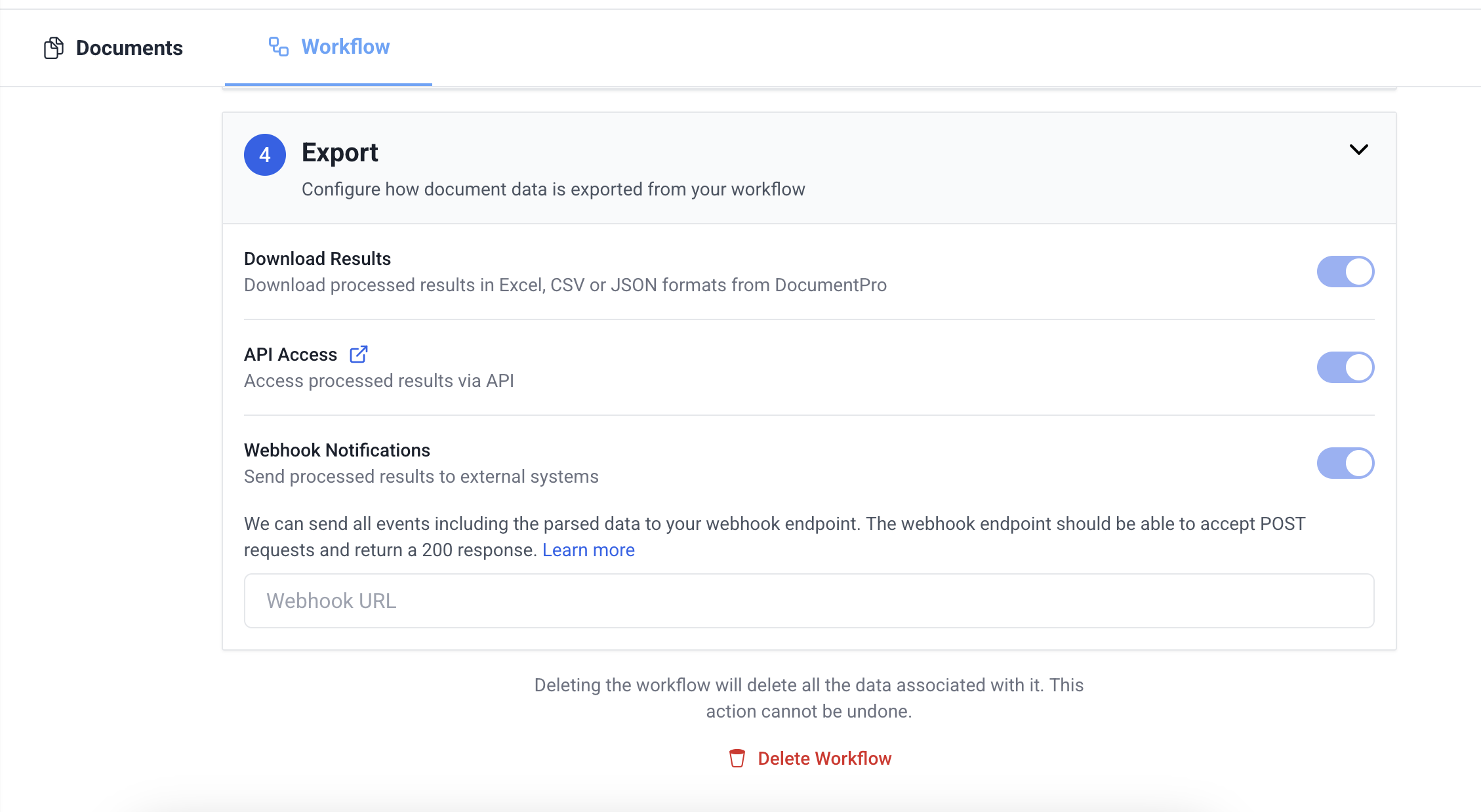
- Navigate to the desired Workflow.
- Go to the "Workflow" tab.
- In the export section, look for the Webhook option.
- Set your Webhook Endpoint and click save.
Webhook Payload
The webhook payload contains an event, timestamp, and data field. Here's an example:
{
"event": "file_request_status_change",
"timestamp": "2024-07-25T14:30:29.565249",
"data": {
"request_id": "a7813466-6f9a-4c33-8128-427e7a4df755",
"request_status": "completed",
"response_body": {
"file_name": "Q2_Financial_Report_2024.pdf",
"file_presigned_url": "https://documentpro-parsed-files.s3.amazonaws.com/Q2_Financial_Report_2024_parsed.pdf?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=...",
"user_error_msg": null,
"template_id": "8e9beda9-5cba-42eb-a70a-b3e5eec9120a",
"template_type": "financial_report",
"template_title": "Quarterly Financial Report Parser",
"num_pages": 15,
"result_json_data": {
"company_name": "TechCorp Innovations Inc.",
"report_period": "Q2 2024",
"financial_highlights": [
{
"month": "April",
"total_revenue": 1250000,
"net_income": 450000,
"earnings_per_share": 2.25,
"operating_cash_flow": 550000
}
]
}
},
"created_at": "2024-07-25T14:30:10.696893",
"updated_at": "2024-07-25T14:30:29.565249"
}
}
The request_status field can be one of: completed, failed, exception, pending, or processing.
When the request_status is completed, the result_json_data field will contain the parsed data.
Example Webhook Implementations
Flask (Python)
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/webhook', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
if request.is_json:
data = request.get_json()
event = data.get('event')
request_status = data.get('data', {}).get('request_status')
print(f'Received event: {event}')
print(f'Received request_status: {request_status}')
# Process the data here as needed
if request_status == 'completed':
parsed_data = data.get('data', {}).get('response_body', {}).get('result_json_data', {})
# Handle the parsed data
print(f'Parsed data: {parsed_data}')
return jsonify({'message': 'Received'}), 200
else:
return jsonify({'error': 'Expected application/json data'}), 400
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
Express (Node.js)
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.post('/webhook', (req, res) => {
const data = req.body;
const event = data.event;
const requestStatus = data.data?.request_status;
console.log(`Received event: ${event}`);
console.log(`Received request_status: ${requestStatus}`);
// Process the data as needed
if (requestStatus === 'completed') {
const parsedData = data.data?.response_body?.result_json_data;
// Handle the parsed data
console.log('Parsed data:', parsedData);
}
res.json({message: 'Received'});
});
app.listen(5000, () => {
console.log('Server is running on port 5000');
});
By implementing webhooks, you can automate your workflow and process parsed data in real-time as soon as it becomes available.